When the video is generated by a CCTV camera, is necessary to compress it to save bandwidth and storage space. The compression is performed by a CCTV codec algorithm such as MJPEG, MPEG-4, H.264 or H.265. In this article I will explain how the main CCTV codecs work. Just keep reading...
A CCTV codec works just like a standard codec created to reduce the video size by looking for redundant information to eliminating it.
We can divide the word CODEC into two parts:
CO = Compression
DEC = Decompression
The side that generates the video will compress it before sending, while the other side that receives it will decompress to display the video correctly in a computer, mobile phone, tablet or other device.
In an analog system, the DVR (Digital Video Recorder) converts the signals from analog to digital and uses an algorithm to compress the video before record it on the Hard Disk (HD) or transmit live to a computer or other device,
Compression in a system with Analog cameras and DVRs

The DVR converts from analog to digital and compress the video by using some CCTV codec algorithm that will discard parts of the video information to save as much storage space as possible.
Compression in a system with IP cameras and NVRs
In an IP CCTV system, the camera is in charge of the video digitization and compression, so it sends the video directly to a NVR (Network Video Recorder) to be recorded in a Hard Disk (HD),

The NVR receives the videos in digital format to recorded it and transmit to a computer which has a specific monitoring software.
But if some information from the digitized video is discarded, part of the quality is lost, right ?
Yes, but the idea is to discard as much information as possible, with minimal impact to the final quality, and each CCTV codec algorithm works in a different way to accomplish this task.
The most common CCTV CODECs are:
- MJPEG: Works with a sequence of images
- MPEG-4: Works with full and partial image variations
- H.264: It is the evolution of MPEG-4 with several improvements
How the MJPEG CODEC works
Let's talk first of MJPEG, which is nothing more than a set of complete images that are sent in a rapid sequence to give the impression of continuous motion.
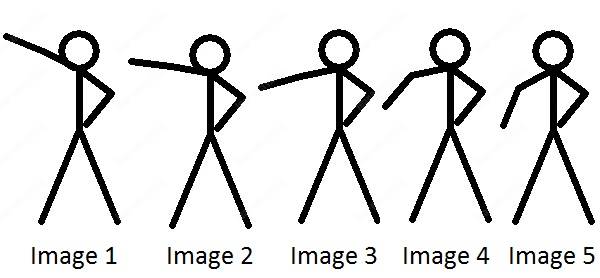
In the this example, we have 5 images that are played in a quick sequence to give us the impression of movement.
If the camera continues with the process of capturing more images is possible to have, more complex movements, such as the animated image below:
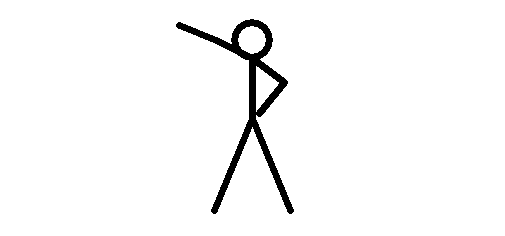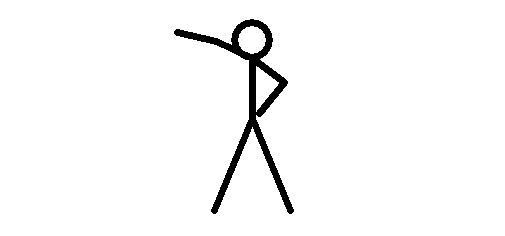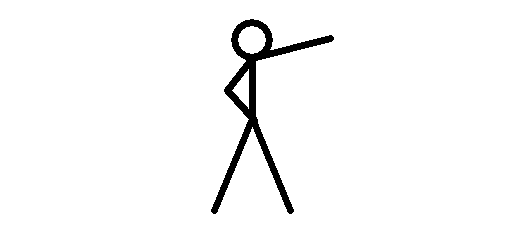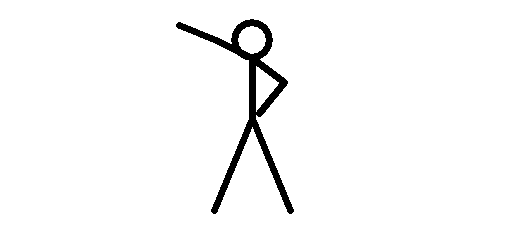
This is the principle of the MJPEG algorithm that sends this sequence of full camera images to the recorder that will play back the images.
The more frames are sent per second, the less "robotization effect" will occur on the video, most CCTV projects are calculated with the use of 15 FPS which is enough to show video with a good quality of movement without spending to much resources on transmission and storage,
How the MPEG-4 CODEC works
With an intelligent way of capturing and sending the video from the camera to the recorder, the MPEG-4 CODEC was designed to capture and send a combination of complete and partial images.
The idea is to save resources by braking the video in complete and partial frames (images) and send them to the receiver (NVR or computer) that is in charge of organize and assembly the video again.

The camera sends the first complete frame (image 1) and then start sending only the moving parts of the image, meaning, the arm in different positions as you can see from images 2 to 5.
How the H.264 CODEC works
H.264 is nothing more than the evolution of MPEG-4, so it uses the same principle, however with an improved algorithm that uses less bandwidth for transmission and storage.
Currently (April/2017) there are already some CCTV manufacturers that use the H.265 CODEC, which compresses the videos even more and soon that will become the new standard for the CCTV market.
Final words about CCTV codec
This is a basic introduction to CCTV CODECs, there are some pros and cons for the MJPEG, MPEG-4, H.264 and H.265 in different types of applications. But in most cases the H.264 is used.
You can find more information about the H.264 codec in the oficial ITU (International Telecommunication Union) website
If you want to learn more about practical CCTV storage calculation read the article: CCTV storage calculation with formula and examples.
Just keep watching the market for the new Kid on the block, H.265 and be aware of its advantage and disadvantages.
==> Here's an update for the new CODEC H.265. I recommend you to read the article H.265 IP cameras benefits (and drawbacks) to learn more.
Now, it's time to contribute with the Blog, please just click the buttons below to share this article.